Security vulnerabilities in IoT applications are unfortunately not uncommon. In order to increase IoT security, more professionals are needed for IoT development. Alternatively, low-code platforms can facilitate app development and ensure security by design in the IoT apps. For this, however, the low-code solutions themselves must meet security requirements.
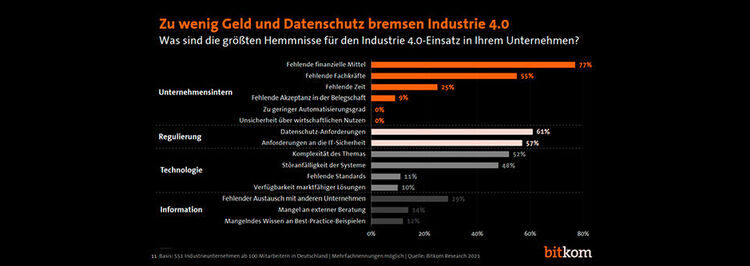
Companies are currently experiencing a large number of obstacles that make the use of Industry 4.0 applications more difficult, according to a Bitkom survey. For example, 77 percent would like to invest more and complain about a lack of financial resources. 61 Percent feel hindered by data protection requirements, 57 percent by IT security requirements.
The barriers to the use of Industry 4.0 applications have practically not changed in recent years, according to the digital association Bitkom. The biggest challenges are the lack of financial resources (77 percent), requirements for data protection (61 percent) and IT security (57 percent) as well as the shortage of skilled workers (55 percent).
“95 Percent of German industrial companies see Industry 4.0 as an opportunity for their own business. The development and use of such solutions is therefore a must for the successful digitization of Germany as a business location,“ says Bitkom Managing Director Dr. Bernhard Rohleder.
However, the IT security requirements of Industry 4.0 and IIoT (Industrial IoT) are complex, and human resources for development and security are notoriously scarce. So that the security of IoT apps can still be improved, new approaches are needed.
Low-code helps with the development of apps
According to the analyst firm Gartner, in the future, professionals outside of IT will develop the majority of technology products and services. By 2024, this should already be the case for 80 percent of technology products and services.
Rajesh Kandaswamy, Distinguished Research vice President at Gartner, also explains how this should be possible: “The growth of digital data, low-code development tools and development supported by artificial intelligence (AI) are among the many factors that make it possible to democratize technology development beyond IT experts.“
The market research house GlobalData sees this in a similar way: the need for digital transformation has therefore accelerated the demand for application development in many industries. However, there is a strong dependence on IT experts or platforms to meet the increasing demand for the creation of new applications. According to GlobalData, it will be low-code no-code (LCNC) platforms that will allow non-IT professionals to accelerate application development faster.
Kiran Raj, Principal Disruptive Tech Analyst at GlobalData, comments: “LCNC technologies can bridge the gaps by breaking down silos between business leaders and IT, enabling non-developers, often referred to as citizen developers, to rapidly develop new applications for various industries, including finance, services, healthcare, manufacturing, retail and technology.“
IoT apps are an important use case of low-code
The Siemens subsidiary Mendix has published the results of the international study “State of Low-Code 2021” on the status quo of low-code technology in the working world: Model-based, visual software development via low-code involves more employees in digitization and is now widely used in various industries. According to the German respondents, the most important areas of application are applications for complex, individual enterprise software (37%), industrial IoT apps (35%), for automated, existing work processes (35%), for data modeling and visualization (34%) and for automated robotic process automation applications (31%).
“With low-code, IoT apps can be developed much faster and more efficiently than with traditional methods,” explains Tino Fliege, Solution Architect at OutSystems. “Because in the low-code cosmos, the creation of applications is not done line by line of code, but with the help of visual modeling: ready-made function blocks can be put together on a graphical interface by drag-and-drop, so that the wheel does not have to be reinvented every time, but developers can fall back on existing standard functions.“
Tino Fliege adds: “Due to extensive configuration options and the possibility to add your own code, the developed IoT shop floor apps can still be tailored to the individual requirements of the respective scenario. The specific connection to the IoT devices used or to IoT platforms such as PTC Thingworx, AWS IoT or Azure IoT is made via standard interfaces, which, for example, the OutSystems low-code platform provides. In this way, the transmitted IoT data from the machines or sensors can be used for any scenarios, for example to prepare and visualize them or to react to events, for example by triggering an emergency shutdown.“
IoT security then also depends on low-code security
A low-code platform can not only make development more independent of the scarce developer resources, since the departments themselves can create the IoT apps. Thanks to the low-code solution, the IoT apps can also be equipped with the necessary security functions, in the spirit of Security by design.
The prerequisite is that the low-code platform itself internalizes security. This is demonstrated, for example, by IoT apps in the automotive sector, where manufacturers and suppliers often process highly sensitive data, such as detailed product information and confidential prototypes. The TISAX test standard of the German Association of the Automotive Industry (VDA), which is based on the ISO 27001 standard, proves that their applications meet a standardized level of protection.
TISAX (Trusted Information Security Assessment Exchange) was developed by the German Association of the Automotive Industry (VDA) in 2017 and has been operated by the ENX Association ever since. It is a test model for a uniform level of information security throughout the entire value creation and supply chain. From manufacturers to suppliers to service providers, it provides a standardized questionnaire and thus enables industry-wide recognition of the test results.
According to TISAX, for example, “Sentry” has been certified by OutSystems. Users of the platform for modern application development can thus rely on the fact that the data processed with the corresponding solution is secure and comprehensively protected, according to OutSystems.
“In an industry as sensitive as the automotive industry, security is a top priority, both physically and digitally,” explains José Casinha, Chief Information Security Officer at OutSystems. “Automotive manufacturing is one of the core industries for German industry – and thus also for our activities on the DACH market. Our goal is to provide comprehensive support to customers in this area and with the TISAX certification, we have continued to invest in this goal.“
It turns out that secure low-code solutions can also provide more security in IoT apps, despite a shortage of specialists in security and programming. Thus, certain obstacles in Industry 4.0 can be eliminated.