The members of the research have managed to develop a neuromorphic chip with a transistor system capable of performing a synapse, thus copying the functioning of a real brain.
The human brain it is compared, technologically speaking, to the hard drive of every human being. It is the most complete organ of our body, reaching more than 100,000 million neurons.
Thanks to technology, the human being is able to create a portable brain using a cluster of microchips. We refer to the case of a team of engineers of the MITwhich has been able to create a chip that emulates the functioning of neurons in the human brain.
To do this, they used classic transistors, called memristors, which allow to create a synapse, the communication between neurons, in an artificial way. These chips are created by an alloy of copper, silver and silicon.
Able to remember images
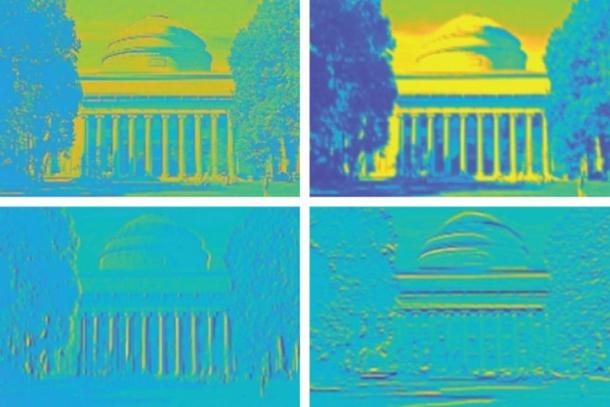
Many projects have been carried out that may be similar, but this chip has been the only one capable of remember images, that is, recover the data stored on the chip for a period of time.
This device has managed to gather thousands of brain synapses in a component that does not reach a centimeter in length.
Memristors allow to create various states leaving aside the binary reading, thus allowing the synapse process. In this way, this portable brain or neuromorphic chip can remember data as images locally, that is, without using the connection to computers.

Valid on any device
Jeehwan Kim, professor of Mechanical Engineering at MIT, explained that ” synapses already exist in software platforms, but, in this case, a neural network has been developed for software systems. Artificial Intelligence available on any portable device.”
For example, the chip can be valid for a smartphone, and even in a vehicle to identify its environment without the need to internet connection. “Memristors can perform these tasks efficiently, without needing to be online,” Kim explained.
This portable brain can provide many functions of learning automatic that could be done immediately.
“We want to develop artificial synapse technology in many image recognition tasks. In the future we will have artificial brains that can perform these tasks without the need for a supercomputer or the so-called cloudKim concluded.