At Harvard, learned to polovinkami microrobotics Wolf | 12.06.2020
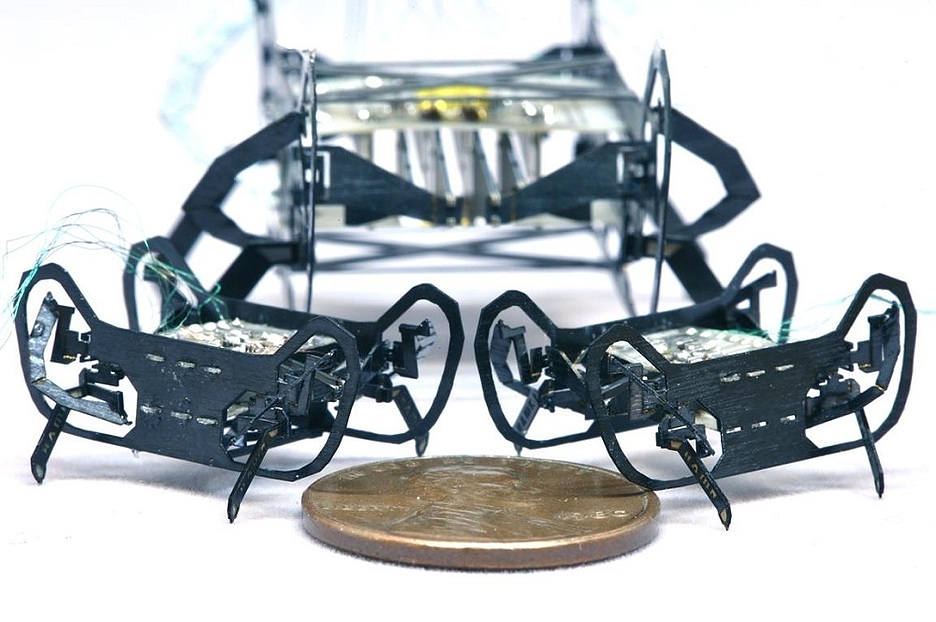
At Harvard have learned to reduce micro-robots, created by the technology HAMR (Harvard Ambulatory MicroRobot). These devices, resembling insects, are collected in three-dimensional structures from two-dimensional
sheets, which are laser cut special contours and details in certain places – bendable, others are connected by hinges.
The first operating prototype of a microrobot assembled HAMR technology, came about seven years ago. He had a length of 4.4 cm. Baby robot conquered the audience with the breadth of its functional
possibilities. He could run, jump, carry heavy loads and even walk on water – with the help of special pads placed on the limbs.
Seven years later he managed to reduce the construction almost doubled to 2.25, see The amazing thing is that this was required to make changes in design, that is, in the basic scheme of the robot. It just
a multiple reduced. Therefore, a breakthrough in Harvard can be called, rather than scientific, and particularly technological. For the creators of a small copy of the robot very important was the fact that the mini-HAMR (HAMR JR)
was almost as fast and agile as its larger prototype.
At Harvard believe that the principle of scaling the design of two-dimensional plates, which is going robot, can be applied to all miniature artificial beings made by
HAMR process. The prospect of HAMR technology is that it is, on the one hand, be much simpler and faster Assembly. On the other hand, HAMR process reduces the number of errors
which is critical in constructing miniature artificial creatures. If you collect little robots in the traditional way – by attaching to each other the various disparate components, almost
any inaccuracy at each stage of Assembly leads to fatal result of malfunction ready device. When using HAMR technology, such risks are significantly reduced.
The disadvantage of the HAMR is the need to use external power sources. But that doesn’t make HAMR-products unsuitable for experiments. On the contrary. It is already actively used for
algorithms development of effective interaction of mini-robots that can increase the productivity of teamwork.
Promising directions of using mini-robots are considered to be agriculture (including the pollination of different crops), monitoring everything from the weather and climatic changes, to
environmental and sanitary situation, as well as rescue operations and many other activities.
Robotics
Journal: Journal IT-News, Subscription to magazines









