San Francisco With a new generation of Starlink satellites, every ordinary smartphone should soon be able to connect to the space Internet. This means that there should be no dead spots in the future – initially in the USA, but in the long term all over the world, Tesla CEO Elon Musk announced in the USA on Thursday evening.
The range of the new technology is limited, but Musk limited it. “They will be able to send text messages,” Musk promised. With particularly good reception, it may even be possible to retrieve videos.
However, the technology is not able to replace conventional mobile networks. The new Starlink network is primarily designed to enable connectivity in regions without any reception.
The reception power of the technology is between two and four megabits per second per radio cell, Musk said. If several devices use the same radio cell, they must share the bandwidth. For comparison: the provider Ookla, which specializes in Internet speeds, estimated the average download rate in mobile communications in Germany in July 2022 at around 53 megabits per second.
Elon Musk and T-Mobile want to bring Internet to remote regions
“This technique will save lives,” Musk said. In the future, people can also call for help in remote regions if they get into trouble: for example, a mountaineer who has an accident, or a traveler who gets into a severe weather. “We assume that this does not require a smartphone to be held in the air, but that the devices will also have reception as normal in your pocket or in your car,” Musk said.
“The beta phase will start at the end of next year,” announced T-Mobile CEO Mike Sievert. “The technology will work with conventional smartphones,” Sievert said. Starlink delivers the satellites. T-Mobile provides the mobile spectrum. There will be no additional costs for end customers, but the service will be included in existing contracts, Sievert promised.
However, Musk announced that the technology will not be limited to T-Mobile in the US, but will be rolled out worldwide. “This is an open invitation to mobile companies around the world: please get in touch with us,” Musk said.
A spokesman for Deutsche Telekom said on request that the cooperation is initially limited to the USA and does not apply to Germany or other Telekom subsidiaries.
The partnership is a win-win for both Starlink and T-Mobile, said Don Kellogg of the consulting firm Recon Analytics. “Musk can open up a new business for Starlink, and T-Mobile can finally close dead spots,” Kellogg said. A number of companies have so far tried to open up satellite Internet to a mass market, but have failed.
“The special thing about the approach is that it should be able to be used with normal mobile phones,” Kellogg told Handelsblatt. First, however, it remains to be seen whether the promises of reception and speed could also be fulfilled.
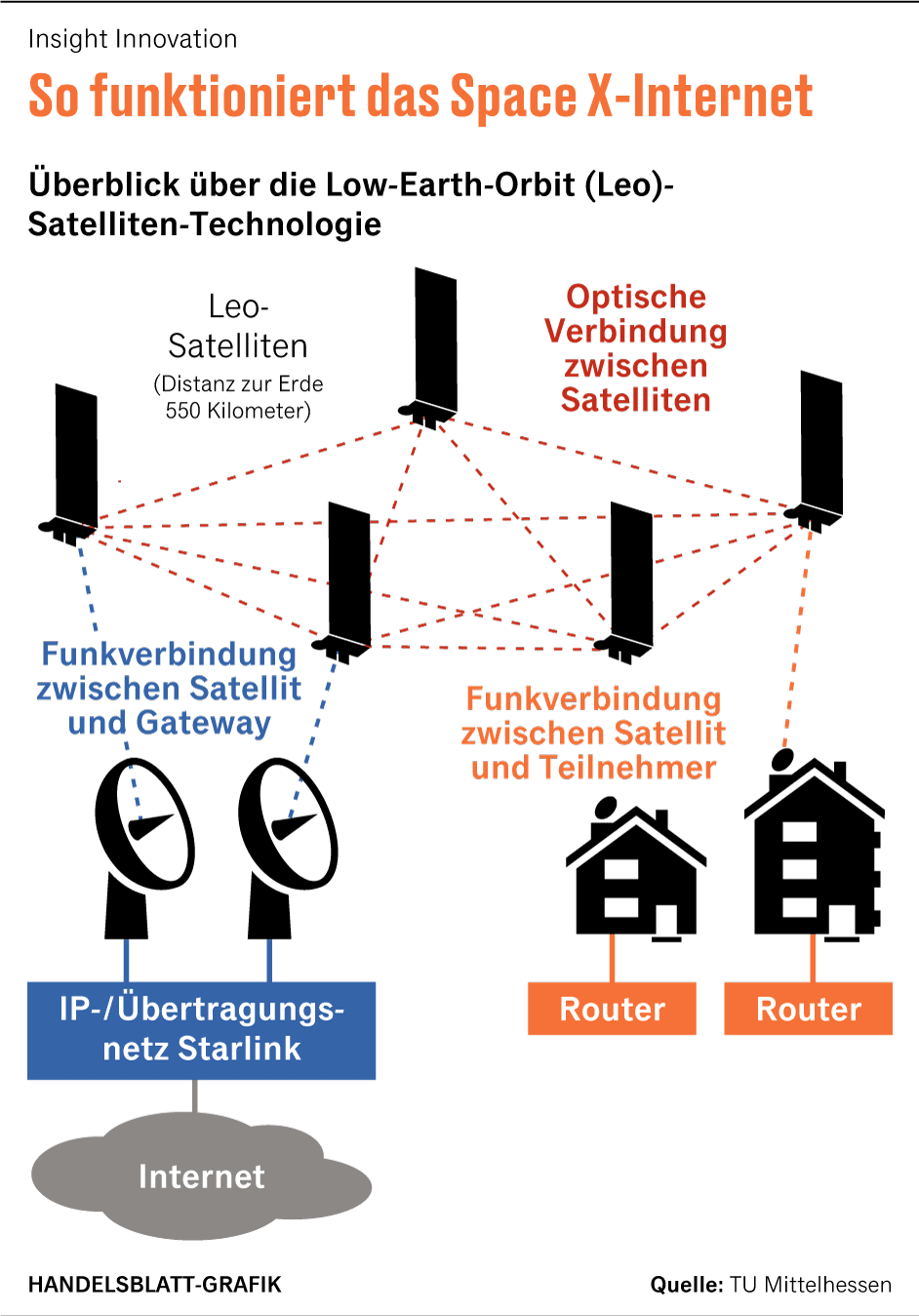
Starlink offers mobile Internet based on satellites in low Earth orbit. Due to the comparatively short distance of around 550 kilometers, the satellites from the “Low Earth Orbit” (Leo) enable a fast Internet signal almost anywhere in the world.
Starlink already has 400,000 customers
The subsidiary of Elon Musk’s satellite company Space X offers its services in more than 30 countries, including Germany. Customers have to purchase a satellite dish for this and then pay a monthly fee. It is currently $ 110 a month in the US, as well as $ 599 for hardware equipment. In May, Starlink announced that it had more than 400,000 paying customers worldwide.
After Starlink had initially offered the services mainly for private households, the company recently received approval in the USA for extended use on boats or in motorhomes. In addition, Starlink now offers a business tariff with improved hardware and higher performance. For this, Starlink demanded $ 500 a month.
The more users Starlink counts in a region, the more Internet speeds can drop. In the United States, Ookla reported that the average download rate of Starlink users fell from 105 megabits per second (Mbps) in the last quarter of 2021 to an average of 91 Mbps in the first quarter of 2022. On the other hand, Starlink promises business customers download rates of up to 350 Mbps.
Most recently, Starlink had experienced a setback. The telecommunications authority FCC had stripped the company of subsidies in the amount of about one billion dollars, with which households in rural areas of the United States should be provided with Internet. Starlink and rival LTD Broadband could not convincingly demonstrate to the authority that they could also deliver the promised services, the FCC said.
U.S. agency cancels Starlink billion-dollar subsidy
FCC Chair Jessica Rosenworcel said, “We cannot afford to subsidize companies that are not delivering the promised speeds or are unlikely to meet the requirements of the program. Rosenworcel added that SpaceX’s technology is “promising”, but stressed that Starlink is still in the “development phase”.
For Starlink, it is also about developing a long-term sustainable business model. The operation of the network is expensive.
The satellites have to be replaced every five to seven years, because they sink and burn up due to the low orbit due to the gravity of the Earth. In total, Musk expects investments of 20 to 30 billion dollars.
The cost of the antennas for the end customers is currently estimated at more than 1000 dollars. The price should fall to $ 500 “in the next generation of devices,” as Musk said. Later, it should drop to $ 300 or $ 250.
Space-X rockets
There are already more than 2,000 satellites in low-Earth orbit for the Starlink network.
(Photo: Bloomberg)
The cooperation with T-Mobile and other mobile phone companies should open up new sources of revenue for Starlink. The focus on stationary antennas could become significantly less important.
Amazon and the EU want to create their own satellite Internet
In addition, Musk is also likely to try to expand his lead over Amazon founder and rival Jeff Bezos. Because he is working on a competitor network to Starlink. Amazon recently announced that it would send 3,236 satellites into low-earth orbit. In 2024, Amazon wants to offer the Internet via satellite, in 2028 it should be fully functional.
Starlink, however, has a few years’ head start. SpaceX has launched more than 2,000 satellites into orbit since 2018.
The EU is also working on a European response to Starlink, because at the beginning of the war, Elon Musk provided the Ukrainians with the services of his satellite network Starlink. The Internet service from space allows Ukrainian soldiers to keep in touch with their commanders even at the most remote sections of the front. The EU could not offer anything comparable.
EU Internal Market Commissioner Thierry Breton proposed the establishment of a separate European Space Internet: “Secure Connectivity Initiative” is the working title. However, the plans are still far behind those of Starlink and Amazon.








